In this article, we are going to learn How to setup a Master/Primary DNS Server with Bind in Redhat/Centos/Fedora. Master DNS Server is Also Referred to as a Primary DNS Server. BIND Stands for ( Berkely Internet Name Domain ) and DNS Server Stands for ( Domain Name System/Server ) is a Service/Protocol used for Resolving the Name to IP Address and IP Address to Name. Master/Primary DNS Server is the main DNS Server where all Name Resolve Databases and Users’ queries are stored and Other DNS Servers ( Secondary DNS Server & Caching DNS Server ) take a query from Master DNS Server.
Let’s take an example: We have millions of websites all over the world and all websites are associated with an IP Address and a Domain name. When we are trying to open a website eg: http://itsmarttricks.com, At the back end DNS finds the IP address associated with that Domain Name and resolves it, and makes available the website in-front of us. We are able to simply remind so many websites just because of DNS, Without DNS we would have to remind all websites by IP Address instead of Name which is almost impossible for us.

Types of DNS Server’s are :
- Caching Only Name Server
Caching Only Name Server is a name server which is stores the DNS Query Information in its own cache for later use.
- Master/Primary DNS Server
Master/Primary DNS Server is the main DNS server where all the database i.e. Zone Files stores and It transfers zone data to other DNS Servers i.e. Slave DNS Servers.
- Secondary/Slave DNS Server
Slave DNS Server is like a Load Balancer of Master/Primary DNS Server which is received zone data from Master DNS Server.
Prepare before Master/Primary DNS Server Configuration :
My Scenario :
- IP Address: 192.168.1.100
- Domain Name: itsmarttricks.com
- Hostname: ns1
- FQDN ( Fully Qualified Domain Name ) : ns1.itsmarttricks.com
Configure the Network Card:
First, we need to configure the network card and assign IP Address, Subnet Mask to our System.
So edit the Network card ( In my case it’s eth0 ), using nano editor as shown below
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
Now enter the below details as shown below ( Highlighted in Blue Color )
# Advanced Micro Devices [AMD] 79c970 [PCnet32 LANCE] DEVICE=eth0 BOOTPROTO=NONE # Replace dhcp with NONE IPADDR=192.168.1.100 # IP Address of the BIND Server NETMASK=255.255.255.0 # Subnet Mask GATEWAY=192.168.1.1 # Gateway DOMAIN="itsmarttricks.com" DNS1=127.0.0.1 # Preferred DNS IP Address ( We can Mention the IP Address of the BIND Server OR LOcalhost i.e. 127.0.0.1 ) HWADDR=00:0C:29:5B:83:74 ONBOOT=yes
Change the Computer Name
Follow the below step to Change the Computer Name. ( Make Changes as shown below Highlighted in Blue Color).
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes NETWORKING_IPV6=no HOSTNAME=ns1.itsmarttricks.com # Hostname of the BIND Server
Configure the DNS Client (/etc/resolv.conf)
After update the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 file the /etc/resolv.conf file would look like this as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf nameserver 127.0.0.1 search itsmarttricks.com [root@localhost ~]#
Configure the hosts File ( /etc/hosts )
Update the host file as shown below (Highlighted in Blue Color)
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/hosts # Do not remove the following line, or various programs # that require network functionality will fail. 127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost ::1 localhost6.localdomain6 localhost6 192.168.1.100 ns1 ns1.itsmarttricks.com
Also Read – How to Configure Slave DNS Server With Bind ( Secondary Dns Server ) In Linux
Follow the below Steps to Configure Primary DNS Server:
Step: 1 Package Required
We need to install Required Packages for Master/Primary DNS Server i.e. :
- bind
- bind-utils
- bind-libs
Follow the below command to install bind, bind-utils, and bind-libs Package.
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install bind
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Setting up Install Process
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: centos.excellmedia.net
* extras: centos.excellmedia.net
* updates: centos.excellmedia.net
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: bind-libs = 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 for package: 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 will be updated
--> Processing Dependency: bind-libs = 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 for package: 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64
---> Package bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be an update
--> Running transaction check
---> Package bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 will be updated
---> Package bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 will be an update
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
======================================================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
======================================================================================================================================
Installing:
bind x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 4.0 M
Updating for dependencies:
bind-libs x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 890 k
bind-utils x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 updates 187 k
Transaction Summary
======================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package(s)
Upgrade 2 Package(s)
Total download size: 5.0 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/3): bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 4.0 MB 03:45
(2/3): bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 890 kB 00:35
(3/3): bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64.rpm | 187 kB 00:08
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 19 kB/s | 5.0 MB 04:32
Running rpm_check_debug
Running Transaction Test
Transaction Test Succeeded
Running Transaction
Updating : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 1/5
Updating : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 2/5
Installing : 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 3/5
Cleanup : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 4/5
Cleanup : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 5/5
Verifying : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 1/5
Verifying : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 2/5
Verifying : 32:bind-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3.x86_64 3/5
Verifying : 32:bind-libs-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 4/5
Verifying : 32:bind-utils-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6.x86_64 5/5
Installed:
bind.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3
Dependency Updated:
bind-libs.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3 bind-utils.x86_64 32:9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6_8.3
Complete!
Step: 2 Create Zones in named.conf File
So we have installed all required Packages, Now we need to configure the main configuration file of the DNS Server i.e. named.conf to create Forward and Reverse Zones, So follow the below steps to do the same.
Now we have to do the required changes in named.conf as per our network and need to create zones by using the decided domain name.
Here below I have mentioned my named.conf file and Highlighted all required changes I did in Blue Color.
[root@localhost ~]# nano /etc/named.conf # Edit the configuration file
//
// named.conf
//
// Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
// server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
options {
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.1.100; }; # IP Address of the Master DNS Server
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query { localhost; 192.168.1.0/24; }; # Allow query in mentioned Subnets
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
### itsmarttricks Internal Zones ###
### Forward Zone ###
zone "itsmarttricks.com" IN { # Domain Name
type master;
file "itsmarttricks.com.for"; # Name of the Forward Zone File
allow-update { none; };
};
### Reverse Zone ###
zone "1.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { # IP Address
type master;
file "itsmarttricks.com.rev"; # Name of the Reverse Zone File
allow-update { none; };
};
After configuring the named.conf file we can check if all the syntax is properly written or not by below command.
[root@localhost ~]# named-checkconf /etc/named.conf
Note: named-checkconf command will not give any output if all syntax is proper, otherwise it will give an error message.
Step : 3 Configure the ZoneFiles
As shown above we have configured named.conf file and created our Forward & Reverse Zones, Now we have to create Zone files as mentioned in Zones i.e. for Forward Zone it’s “itsmarttricks.com.for” and for Reverse Zone it’s “itsmarttricks.com.rev“, So follow the below steps to do the same.
To Create Zone files we have to copy some sample files as per our zone name which is located at /var/named.
So copy the named.localhost file as itsmarttricks.com.for for Forward Zone & named.loopback as itsmarttricks.com.rev for Reverse Zone as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/named/ [root@localhost named]# ls -l total 28 drwxrwx---. 2 named named 4096 Nov 2 08:53 data drwxrwx---. 2 named named 4096 Nov 2 08:53 dynamic -rw-r-----. 1 root named 3171 Jan 11 2016 named.ca -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Dec 15 2009 named.empty -rw-r-----. 1 root named 152 Jun 21 2007 named.localhost -rw-r-----. 1 root named 168 Dec 15 2009 named.loopback drwxrwx---. 2 named named 4096 Nov 2 08:53 slaves
[root@localhost named]# cp named.localhost itsmarttricks.com.for [root@localhost named]# cp named.loopback itsmarttricks.com.rev
As shown above, we have created our zone files in /var/named, Now we have to Configure both zone file as per our requirement, So follow the below steps.
First, we are going to Configure the Forward Zone.
Before Configuration, the file would look like this as shown below.
$TTL 1D
@ IN SOA @ rname.invalid. (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS @
A 127.0.0.1
AAAA ::1
After Configuration the file would look like as shown below :
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA ns1.itsmarttricks.com. root@ns1.itsmarttricks.com. (
2010031403 ; serial
3600 ; refresh
1800 ; retry
604800 ; expire
86400 ) ; minimum
; name servers
@ IN NS ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
; name server A records
ns1 IN A 192.168.1.100
itsmarttricks.com. IN A 192.168.1.100
; mail exchanger record (MX record)
IN MX 5 ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
; host and canonical name records
mail IN CNAME ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
www IN A 192.168.1.100
ftp IN A 192.168.1.100
After configuring the itsmarttricks.com.for file we can check if all the syntax is properly written or not by below command.
[root@localhost ~]# named-checkzone itsmarttricks.com /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.for zone itsmarttricks.com/IN: loaded serial 2010031403 OK
Now let’s configure the Reverse Zone.
Before Configuration, the file would look like this as shown below.
$TTL 1D
@ IN SOA @ rname.invalid. (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS @
A 127.0.0.1
AAAA ::1
PTR localhost.
After Configuration the file would look like as shown below :
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA ns1.itsmarttricks.com. root@ns1.itsmarttricks.com (
2010031402 ; serial
28800 ; refresh
14400 ; retry
3600000 ; expire
86400 ) ; minimum
; name servers
IN NS ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
; name server A records
ns1 IN A 192.168.1.100
; PTR records
100 IN PTR ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
After configuring the itsmarttricks.com.rev file we can check if all the syntax is properly written or not by below command.
[root@localhost ~]# named-checkzone itsmarttricks.com /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.rev zone itsmarttricks.com/IN: loaded serial 2010031402 OK
Zonefile Records with Explanation :
- SOA – Start of authority
- NS – name server
- A – host record (name to IP)
- IN – internet type of record
- CNAME – canonical name (alias)
- MX – mail exchange
root.ns1.itsmarttricks.com. – The email address of the responsible person to whom u can email about the DNS query.
Serial – it is given for the slave DNS server when the slave DNS server contacts the master DNS server for updatation. it looks for this Serial Number. If the master DNS server is having a greater serial number than a slave, then the only slaves will download those changes on the slave DNS server.
3H – Refresh Rate: After every 3 hours slave will contact the master DNS server for updations.
5M – Retry: if the slave is not able to contact master DNS then after 15 minutes it will retry to contact master DNS server for updations.
1W – Information that is available with slave will expire after 1 week.
TTL 86400 – ( Time to live cache information ) – Cache Information with master DNS server will expire after 86400 seconds.
PTR – pointer records mean IP to name resolutions.
Now change the ownership of the file to root.named by using chown command as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# chown root.named /etc/named.conf [root@localhost ~]# chown root.named /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.for [root@localhost ~]# chown root.named /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.rev
As shown below all files i.e. named.conf, itsmarttricks.com.for, itsmarttricks.com.rev are owned by root.named.
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /etc/named.conf -rw-r-----. 1 root named 1484 Jan 1 07:03 /etc/named.conf [root@localhost ~]# ls -l /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.for -rw-r-----. 1 root named 542 Jan 1 09:17 /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.for [root@localhost ~]# ls -l /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.rev -rw-r-----. 1 root named 347 Jan 1 09:25 /var/named/itsmarttricks.com.rev
Now Start the DNS Service.
[root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/named start Generating /etc/rndc.key: [ OK ] Starting named: [ OK ]
We have to start the DNS service at a startup to start the service automatically when we restart the server, follow the below step to do the same.
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 35 named on [root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --list named named 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
So we have successfully configured the BIND DNS Service, Now it’s time for testing., We have tools like dig, nslookup to check the DNS service working status. So the Command would look like as mentioned below.
dig <FQDN ( Fully Qualified Domain Name/IP Address )> i.e. dig ns1.itsmarttricks.com

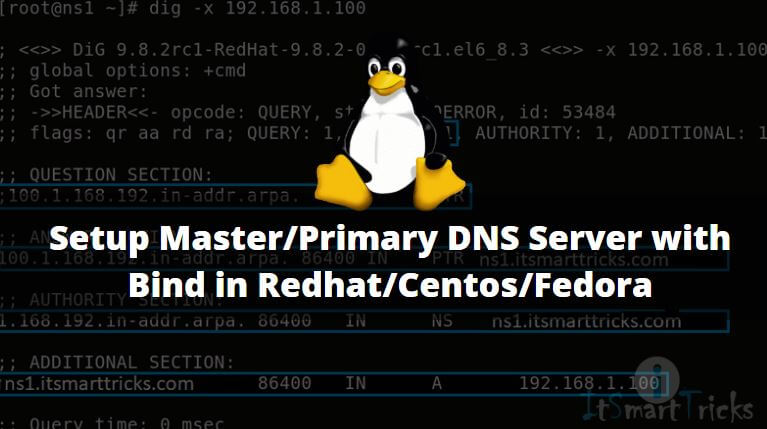
Now let’s check for IP Resolution i.e. dig -x 192.168.1.100

We can use the nslookup command to check DNS Service is working properly or not as shown below.
[root@localhost ~]# nslookup itsmarttricks.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Name: itsmarttricks.com Address: 192.168.1.100 [root@localhost ~]# nslookup ns1.itsmarttricks.com Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 Name: ns1.itsmarttricks.com Address: 192.168.1.100 [root@localhost ~]# nslookup 192.168.1.100 Server: 127.0.0.1 Address: 127.0.0.1#53 100.1.168.192.in-addr.ar pa name = ns1.itsmarttricks.com.
So everything looks good and the Master/Primary DNS Server is working fine as shown on the testing output above. on our next article I will explain How to Configure Slave DNS Server till then stay tuned to itsmarttricks.com.
That’s all, In this article, we have explained How to Setup Master/Primary DNS Server with Bind in Redhat/Centos/Fedora. I hope you enjoy this article. If you like this article, then just share it. If you have any questions about this article, please comment.